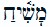“Are they really bringing people to workplaces to give them a better life?”
It was known or said that even if Jews were converted to the Christian faith, they remained “different” because of their bloodline. It was also known that many were jealous for the lifestyle and family feeling which could be found in the Klal Yisrael or Jewish communities. Many goyim found the Jews separated themselves from the society, but they did not often see it were goyim who themselves gave enough reason not to mix too much with them.
Samuel Morgenstern was one of those shopkeepers who was one of the most loyal buyers of Hitler’s paintings in Vienna, by which Hitler could receive enough money not to be a tramp. Naturally there were also rumours Hitler could not stand Jews because he got a disease from regularly going to some ‘Jewish harlots’.

Portrait of Karl Lueger (ca. 1900), mayor of Vienna. He used anti-Semitism as a political strategy. Collection: Austrian National Library / painter: Alois Delug. Source: Wikimedia Commons. Rights: Public Domain

Mein Kampf, (German: “My Struggle”) political manifesto written by Adolf Hitler. It was his only complete book and became the bible of National Socialism (Nazism) in Germany’s Third Reich. It was published in two volumes in 1925 and 1927, and an abridged edition appeared in 1930. By 1939 it had sold 5,200,000 copies and had been translated into 11 languages.
It perhaps were not just rumours that the politician, co-founder and leader of the Austrian Christian Social Party, and mayor of Vienna Karl Lueger (1844-1910), used anti-Semitism as a political strategy, and that he was also praised as “the greatest German mayor of all time” by Adolf Hitler (In Mein Kampf) who did not mind following his ideas.
The prejudices about the role of the Jews in the Great War were incorrect, but as with many rumours, it spread like a virus. Many Germans did not want to believe how more than one hundred thousand German and Austrian Jews had fought for their homeland, one of them being Otto Frank, the German-born merchant best known as the father of Anne Frank, who witnessed the Battle of the Somme in 1916.
In the 1920ies our family members could already hear how our brethren were compared with germs. It was as if our people had been infecting generations for ages. That Hitler never thought his people were not strong enough to live according to the wishes of their god or according to the mitzvot of the Only One True God, the Elohim Hashem Jehovah. Lots of our friends could not believe that those who said they were “Christian” and as such would, or should, be following the Nazarene Jewish rabbi who preached brotherly love, could do such atrocious things, as others told about them. Perhaps it was to set up Jehudiem against Christians, so that the goyim had all the reason to tell
The words spread that Hitler said that you cannot fight a disease without destroying the person who caused it, and as such according to him, the influence of the Jews would never disappear without removing the perpetrator, the Jude, from the midst of the Arian race.
Radical ideas paved the way for the mass murder of the Jews in the 1940s, but not many of the Bnei Yisroel or Chosen People of God wanted to believe the rumours at first.
In many families, like ours, it was the saying
“the Soup will not be eaten as hot as it is served”.
They heard about plans which would be taken, but they seemed so unbelievable that they could not be true or would have been exaggerated, as by a circling fire. Others were not so much at ease, and warned
“to be aware of a silent dog and still water”.
Should we look askance at him? Now we can easily say they had much better looked at him out of the tail of their eyes. By not believing the many rumours, lots were woken up with a start, when it was too late.
For a long time, many wondered if it was within the odds, whilst others said
“He is not likely to go.”
Others wanted to be a friend to all, forgetting that then they would be a friend to none. Many debates about what went on in Germany and Austria could bring lots of talks after the children were sent to bed. For sure that what was to be spoken about was not for children’s ears.
It was, and is still, known that there was and is, an existing prejudice that Jews associate with financial power and monetary gain. Many are also convinced Jews are “foefelaars“, who make their pile on the poor white people. Lots of Jews may be looked at as a ramay / nokhel, a fiddler or cheater whilst there was no oysnarn at all.

White movement propaganda poster from the Russian Civil War era (1919), a caricature of Leon Trotsky, who was viewed as a symbol of Jewish Bolshevism.
In many countries people also looked at the Jehudi as the originators or conspirators and spreaders of communism. The vast majority of the communist leaders at that time were Jewish. However, it is only a small part of the Jews that were communists, and what a lot of people did not see is that several Jews were promoting or aiming for social equality, this being considered by many liberals and capitalists a danger for the economy and consumption gain. During the war with the Soviet Union, from 1941 on, it will be the idea of the ‘Jewish communism’ (sometimes also called Marxian-communism or meant to be Jewish Bolshevism, also Judeo–Bolshevism) with terrible consequences. The population and the prisoners of war being brutally treated by the Germans.
When Hitler got into power rumours got stronger, but still many did not want to believe what went around. Others were smart enough to be at the safe site by sending their beloved far away from Germany and Austria. Some thought they would be safe in Holland, but how they were mistaken. Having gone to Holland luckily several managed to cross the channel and find a safe haven in the United Kingdom, but the others got taken and deported.

At the Schalkland, in the “Klein-Brabant” region, less than 25 kilometres from the centre of Brussels and 19 kilometres from Antwerp, to the south of the Dendermonde highway (Mechelen – Dendermonde) was build the “Willebroeck Fort” as a fortified defence to protect the port and city of Antwerp, which by Royal Order dated 12 January 1907 rechristened the fort “Breendonck Fort”. On september 20th 1940 Sturmbannführer Philip Schmitt brought his first victims to Breendonk. The Fort officially became the Auffanglager Breendonk, a transit camp; a major centre for the Sicherheitspolizei-Sicherheitsdienst (SIPO/SD), the german political police.
Words spread that in Breendonk the kaze-the mats were to be removed from the earth in which they were covered. Three or four men had to push a railway carriage that was loaded with the earth. It was not the best marterial the prisoners had to use. Of these vehicles, the wheels were worn out, having to be pushed on worn-out rails, so that a person would have more than it is possible. Was it a rumour or was it true that the SS guards, with their weapons beated on the upper arms, the backs of the heads of the unfortunate ones until the latter were exhausted, but also fell dead?

Former working site at the camp of Breendonk. The regime set up here by the Nazis hardly differed from that of an official concentration camp. The undernourishment and the forced labour wore down the body and mind. The ever-present physical cruelty sometimes caused the death of prisoners. Initially, the camp was only guarded by a few German SS and a detachment of the Wehrmacht. In September 1941, the Wachtgruppe of the SD arrived as back up. This time, these were no longer German SS but mainly Flemings.
Some of the prisoners were to be buried up to the neck, after they were first on a ferocious manner, beaten. The S, S. jailers were there, then settled for the pitiful earth at the face of them. The game lasted sometimes for 1 or 2 hours, and when the victims were about to die, they did not stop to punch and to death. During the singing of the song of Breendonk, the text of which these words were placed on the grave:
” Wir werden nie mehr Breendonk vergessen, das Paradies-tier Juden…’.”
Sturmbannführer (majoor) Schmitt had created and placed a pulley on the ceiling in a folterbunker (torture bunker or blockhouse) of the camp, to make, that the victim’s hands at the back tied up would be drawn to the ceiling.
After that, it was a pizzle of the shot, he was then beaten with a bullepees (bullenpees: baton between a whip and a stick made from dried penis of a bull). When the hoist was released, the unfortunate person fell on two angular boards. Kachelpoken or stove pokers were glowed for immediate use,… because the Jews were not worth the bullet. They had to be sent to death during work and by torture.
When the words rang true for most of the Jews still living in the region, it was too late to find a safe place for their children and for themselves.

After the camps in Belgium or Holland as “Musselmen” (completely emaciated) thousands were deported to Germany to find an end to their unbearable suffering, either of starvation, giving up, or in the gas chambers.
The remaining Jews in Belgium were unable to follow the course of events that their fellow believers underwent elsewhere. Their own concerns were too overwhelming for this and contact with neighbouring countries was too incomplete. The seeping job tidings were considered exaggerated …
Commissioned by the notorious member of Heinrich Himmler’s SS, the Nazi paramilitary corps, Adolf Eichmann, the Sicherheits polizei in Berlin, wrote the following urgent letter, in which the word “Secret” is not missing (22 June 1942):
“From mid-July and early August this year, special trains of 1,000 people each day are planned, first of all about 40,000 Jews from the occupied French territory,
Send 40,000 Jews from the Netherlands and 10,000 Jews from Belgium to employment in the Auschwitz camp.
“The circle of persons to be included extends primarily to Jews who are skilled in work, insofar as they do not live in mixed marriages and do not have the nationality of the British Empire, of the U.S.A., of Mexico, from the enemy states, from Central and South America, as well as from the neutral and related states.“I may request willing access and assume that there are no objections to these measures on the part of the foreign office either.
Commissioned get. Eichman “
On 12 July 1942 the last restriction on freedom before the local raids started was put visible on billboards. From the onward Jews were no longer allowed to visit cinemas, theatres, sports grounds or public institutions. In the trams they were only allowed to stand on the front platform of the trailer.
Such regulations still did not unbalance many of the Jewish diluted community. According to many the German measures only wanted to deprive the Jews of public pleasures … (Few will then have immediately known that the first nocturnal masses in Paris on Friday July 17, 1942 raffle had taken place.)

Pennant for Organisation Todt

Woman with Ostarbeiter OT badge at Auschwitz
The second Jewish labour team was also confidently leaving the civil and military engineering organisation “Organization Todt” to Charleville-Mèzières (18 July), until on July 22 the second deception beared its bitter fruit.(It was the day that the memorial of the destruction of the Temple took place in Jerusalem in the evening – Tischa be’af – -). Jews were arrested without any excuse! When that day the trains from Brussels and Antwerp stopped at Mechelen as usual, Feldgendarmen were on the platform. All the Jews, both men and women, were taken out. The same happened at the Antwerp and Brussels North terminus stations. (The Brussels-North-South connection did not yet exist.) Their freedom had ended. Some went to Breendonk. Most were sent to the 18th century Dossin barracks, where between 1942 and 1944, 25,484 Jews, 352 Roma and Sinti were deported. Just over 5% returned from Auschwitz-Birkenau.
Kazerne Dossin, Goswin de Stassartstraat 153, B. 2800 Mechelen, where in the old barracks, visitors will find a memorial, which commemorates countless people who stayed there in despair and fear and who died later in unspeakable circumstances.
From the onward the Jews throughout Belgium were being seized by panic. Being an ode alone was therefore sufficient here to be arrested … The Jewish Council was powerless … followed by a reaction of partial sobering among the Jewish population. They forged new flight plans that were kept secret even from close acquaintances.
The panic mood was tempered after a few days. When people received mail from the internees in Mechelen it all looked not as bad as the rumours went around.
They are not nearly as bad there … Fruits are missing … They may receive packages …

Faces from those who lost their life after being brought to the Dosin Kazerne in Mechelen
These days we remember all those who lost their life in a struggle to survive in a hatefull world.
Let us not forget how politicians can use disinformation and propaganda to mislead many and to create unwanted scapegoats.
We also may not let ourselves be fooled this time that it would not be as bad today with what was happening in the 1930ies. There are people who say
That can never repeat again
but after the Great War all people agreed also that such a horror should never take place again. Only a few years later the world found itself again in such time or terror.
This time let us be more careful, notice the signs of people bringing others on the wrong path, and react wisely to those who want us to believe we are ridiculous seeing ghosts or bad things in what are just jokes or carnavalesc activities.
+
Preceding
Remembrance and freedom in the Netherlands – Dodenherdenking and Bevrijdingsdag
Niet te negeren gebeurtenissen rond Joden in België
The danger of having less than 25 000 Jews in Belgium
++





 Demand for recognition of one’s identity is a master concept that unifies much of what is going on in world politics today. In his new
Demand for recognition of one’s identity is a master concept that unifies much of what is going on in world politics today. In his new