
American political scientist, political economist, and author Yoshihiro Francis Fukuyama in 2015
The American writer and political theorist Francis Fukuyama wrote
“Human beings never existed in a pre-social state. The idea that human beings at one time existed as isolated individuals is not correct.”
In his seminal 1989 essay ‘The End of History?’ he also wrote
‘What we may be witnessing is the end point of mankind’s ideological evolution and the universalization of Western liberal democracy as the final form of human government.’
Fukuyama trying to convey silent messages through stories about the evolution of democratic societies he continued
‘With the fall of the Soviet Union the struggle for recognition, the willingness to risk one’s life for a purely abstract goal, the worldwide ideological struggle that called forth daring, courage, imagination, and idealism will be replaced by economic calculation, the endless solving of technical problems, environmental concerns, and the satisfaction of sophisticated consumer demands.’

The End of History and the Last Man is a 1992 book by Francis Fukuyama, expanding on his 1989 essay “The End of History?”, published in the international affairs journal The National Interest.
Fukuyama did not suggest that the end of history meant the end of wars or conflicts, but rather that capitalism and Western-style liberal democracy were the culmination of human political development and would not, and could not, be transcended. He beliefs that the triumph of liberal democracy at the end of the Cold War marked the last ideological stage in the progression of human history. The initial political challenge having to escape beyond tribalism and the “tyranny of cousins”.
For Fukuyama, tribal organisation responds to structural imperatives in social evolution but also blocks the path to further development. The early account of the origins of state-like forms relies heavily on Lawrence Keeley’s military-focused argument in War Before Civilisation (1996) and does not consider the evidence assembled by Keith Otterbein in How War Began (2004): that warfare greatly declined in importance following the hunting to extinction of the larger mammals. Keeley himself grants that early settlement cultures, such as the Natufian,
“furnish no indication of warfare at all”. {Robin Blackburn– The Origins of Political Order: From Pre-Human Times to the French Revolution, By Francis Fukuyama}
We can see that in the West the majority prefers a capitalist system and in several industrialised countries people are a lot afraid of what smells social or communist. Fukuyama thinks that all states are going to adopt a form of capitalist liberal democracy. It was an argument contested from almost the moment he finished writing his essay.
The rise of Islamism, the unleashing of ethnic conflicts, the challenge posed by China – a myriad developments, his critics suggested, questioned the presumption of an end of history.
Donald Trump’s Presidential victory was one of the signs how politicians would easily be able to lure people in false ideas, by their words. The last few years we have seen a seemingly unstoppable rise of populist forces throughout Europe.
Many will probably see how in the quarter of a century since Fukuyama wrote his essay, politics, particularly in the West, has indeed shifted away from ‘ideological struggle’ towards
‘the endless solving of technical problems’.
The broad ideological divides that characterized politics for much of the past two hundred years have been eroded. Politics has become less about competing visions of the kinds of society people want than a debate about how best to manage the existing political system, a question more of technocratic management rather than of social transformation.
What might more come to an end is the believe of people in political systems and in politicians. Lots of people are convinced that politicians are not listening to them and are mostly just working for themselves and trying to get the best paid job.
The majority of politicians have lost connection with the ordinary people who want to feel as if they are justly recognised and that their voice can be heard. The last few years they feel more they are mocked at, nobody taking their voice seriously. Politicians should come to know that this desire to experience both personal and collective recognition is inescapable to the modern human condition.
Liberal democratic states that Fukuyama so vigorously defended in “The End of History” have not responded well to the challenges of pluralism.
After the collapse of the Soviet Union, few believed in an alternative to capitalism, not seeing that the Soviet Union was not really the best representative of communism, because it had more dictators than real communist leaders. Communist parties crumbled, while social democratic parties remade themselves, cutting ties to their traditional working class constituencies while reorienting themselves as technocratic parties. Trade unions weakened and social justice campaigns eroded.
It seemed that not only in Europe social movements and political organizations eroded, and the far-right movements gained space. Local people wanted to become recognised and wanted to look upon social change through the lens of their own cultures, identities, goals and ideals.
Many sections of the working class have found themselves politically voiceless at the very time their lives have become more precarious, as jobs have declined, public services savaged, austerity imposed, and inequality risen. Many also came to see all those immigrants as a danger for their own position, their jobs and income as well as being afraid of loosing their culture.
Having their world coming to an end.
Lots of people in charge of the working of society did not see the discontent many their votes expressed.

Prominent alt-rightists were instrumental in organising the “Unite the Right” rally in Charlottesville, Virginia in August 2017. Here, rally participants carry Confederate battle flags, Gadsden flags and a Nazi flag.
In Europe and America, people have become disaffected with the old order and felt more attraction for those who promised heaven on earth and for them “a great nation” again. Many of the opposition movements that give voice to that disaffection of the labourers, are shaped not by progressive ideals but by sectarian politics, and rooted in religious or ethnic identity. The Islamist AKP in Turkey or the Hindu nationalist BJP in India are the equivalents of the Front National in France or the alt right, far-right, white supremacist, white nationalist, white separatist, anti-immigration and antisemitic movement in America and Europe.
Those growing right-wing and far- or extreme-right-wing groups should make us aware of the severity of the present political situation. We are witnessing a globally disinformation movement which is creating more hatred and racism as well setting up people against others for wrong reasons.
The current tumult is the result of struggles for recognition that remain unshaped by progressive movements, of ideological struggles in a post-ideological world.
 Demand for recognition of one’s identity is a master concept that unifies much of what is going on in world politics today. In his new book: Identity: The Demand for Dignity and the Politics of Resentment Francis Fukuyama looks at the new layers of meaning of the voters or citizen’s identity.
Demand for recognition of one’s identity is a master concept that unifies much of what is going on in world politics today. In his new book: Identity: The Demand for Dignity and the Politics of Resentment Francis Fukuyama looks at the new layers of meaning of the voters or citizen’s identity.
Fukuyama believes that the focus on self separates people from their communities. The demand for identity cannot be transcended and therefore people must begin to shape identity in a way that supports rather than undermines democracy.
When coming to know the self one can not ignore the connection with religious feelings. One aspect of wisdom is recognizing your need for The One Being outside man.
Christianity succeeds in diminishing family ties when the Church takes a strong stand against practices which enhanced the power of lineages such as cousin marriage, divorce, adoption and marriage to the widows of dead relatives. The looser family pattern favoured by the practices of Latin Christianity have the effect of channelling assets to the Church itself (eg through widows’ bequests). Fukuyama further urges that “contrary to Marx, capitalism was the consequence rather than the cause of a change in social relationships”. Yet he soon acknowledges that
“the most convincing argument for the shift has been given by the social anthropologist Jack Goody“,
an authority whose work could be seen as a distinctive fruit of Cambridge Marxism. {Robin Blackburn– The Origins of Political Order: From Pre-Human Times to the French Revolution, By Francis Fukuyama}
Fukuyama has the idea that the individualistic sense of identity comes to the fore during periods of modernisation in which people fled from rural areas into the cities and were confronted with a mass of different dialects or languages, religions and cultures and were aware of a sense of the difference between where they were and where they are now. Today in some way many people seem to be lost or are so much afraid of such confrontation they do hope their politicians can solve that problem of difference between the inhabitants of their villages, cities and countries.
Fukuyama notes the ways in which questions of identity politics have come to be regarded as synonymous with the right. Donald Trump supporters are animated around the removal of Confederate statues and the president’s lack of defence to political correctness is a significant mobilising force on the right.
Intimidation and efforts to control people have become the present day norm for many politicians, who gain a lot of popularity because many fall for their lies. That virus threatening democracy has not only infected the United States but also the European Union. As such we may see that identity politics has become the political form of cultural fragmentation of these days, and is corrosive of some features of an effective democracy – social cohesion, talking with strangers and working across the aisle.
According to me the politicians do have to give an identity to the people again and have to show them that we all have more in common with each other than what divides us.
It is a “we” who are the same, and not a “we” who are strangers dwelling together despite our differences. {Jeff Rich – Identity Crisis – some theses on identity politics}

History shall continue and show how man tries to find different political solutions and ways to govern a country. Man shall have to find a way to make it that by the globalisation more and more people would be going to see the richness of a multicultural society, instead of fearing it.
+
Read also
- Our political systems and juggling with human laws
- Declaration of war against Islam and Christianity
- Declining commitment to democracy : What’s going on around the world ?
- Collision course of socialist and capitalist worlds
- Subcutaneous power for humanity 2 1950-2010 Post war generations
- The Free Market (and all that) did not bring down the Berlin Wall
- Common Goods, people and the Market
- Pushing people in a corner danger for indoctrination and loss of democratic values
- Populism endangering democracy
- An European alliance or a populist alliance
- British Parliament hostage its citizens for even more months
- American social perception, classes and fear mongering
- United in an open society relying not on command and control but on freedom
- Capitalism and economic policy and Christian survey
+++
Further related
- The Origins of Political Order: From Pre-Human Times to the French Revolution, By Francis Fukuyama
- What Do We Mean When We Say Something Is Political? — Recommended Readings
- The Sisyphean Task at the Core of Identity Politics
- Fukuyama has a new book on identity
- Little Theories
- The Decline of Liberalism
- Identity
- Identity Crisis – some theses on identity politics
- We’re in This Together Now
- Two Books by Francis Fukuyama
- What Fukuyama got right.
- From ‘End Of History’ To ‘End Of Democracy’ – Why Fukuyama Now Likes China
- “Echoing Margaret Thatcher’s dictum that ‘there is no alternative’ …
- Social Psychology and Religious Behavior
- Francis Fukuyama and technology
- Eurasianism: The Struggle For The Multi-Polar World

























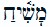






























Pingback: What a 21st century civil war would look like | Marcus Ampe's Space
Pingback: Economic pain for all or for the poorer majority – Some View on the World
Pingback: Much news — and too many voices | Marcus Ampe's Space
Pingback: How willing are people to stand up for their values and beliefs – Some View on the World
Pingback: Significant results of investigations concerning election preference in the UK | Marcus Ampe's Space
Pingback: Is the situation within the United States really as bad as Donald Trump makes it seem? | Marcus Ampe's Space